
Securing your financial future means more than just saving and investing—it also means protecting your loved ones from the financial impact of life’s uncertainties. Life insurance is the cornerstone of any robust financial plan, yet it remains misunderstood by many. This guide will walk you through the essentials of life insurance, demystify key terms, outline the main types of policies and help you choose the right coverage based on your unique needs.
Why Life Insurance Matters
Financial Protection for Dependents
If you are the primary earner in your household, your sudden absence could leave your family struggling to meet day-to-day expenses, mortgage payments, children’s education costs and other long-term goals. A life insurance policy ensures that your dependents continue to receive financial support even if you’re no longer there to provide for them.
Debt Repayment and Estate Planning
Outstanding liabilities—home loans, personal loans, credit card balances etc. don’t disappear when you pass away. Life insurance proceeds can be used to clear debts and preventing creditors from burdening your family. Additionally, life cover can be a key component of your estate plan, it is providing liquidity to pay estate taxes or fund inheritances.
Peace of Mind
Knowing you have a safety net in place alleviates stress and allows you to focus on achieving other financial goals like retirement planning, wealth accumulation or funding your children’s higher education.
Key Life Insurance Terms
Before diving into policy types, familiarize yourself with these fundamental terms:
- Sum Assured: The guaranteed death benefit payable to beneficiaries
- Premium: The regular payment you make (monthly/quarterly/annually) to keep the policy in force
- Policy Term: The duration for which your policy remains active
- Maturity Benefit: Lump sum paid to you if you survive the policy term (in endowment and ULIP plans)
- Rider: Additional coverage add-ons such as critical illness rider or accidental death benefit
- Free Look Period: Initial window (usually 15–30 days) to review and cancel without penalty
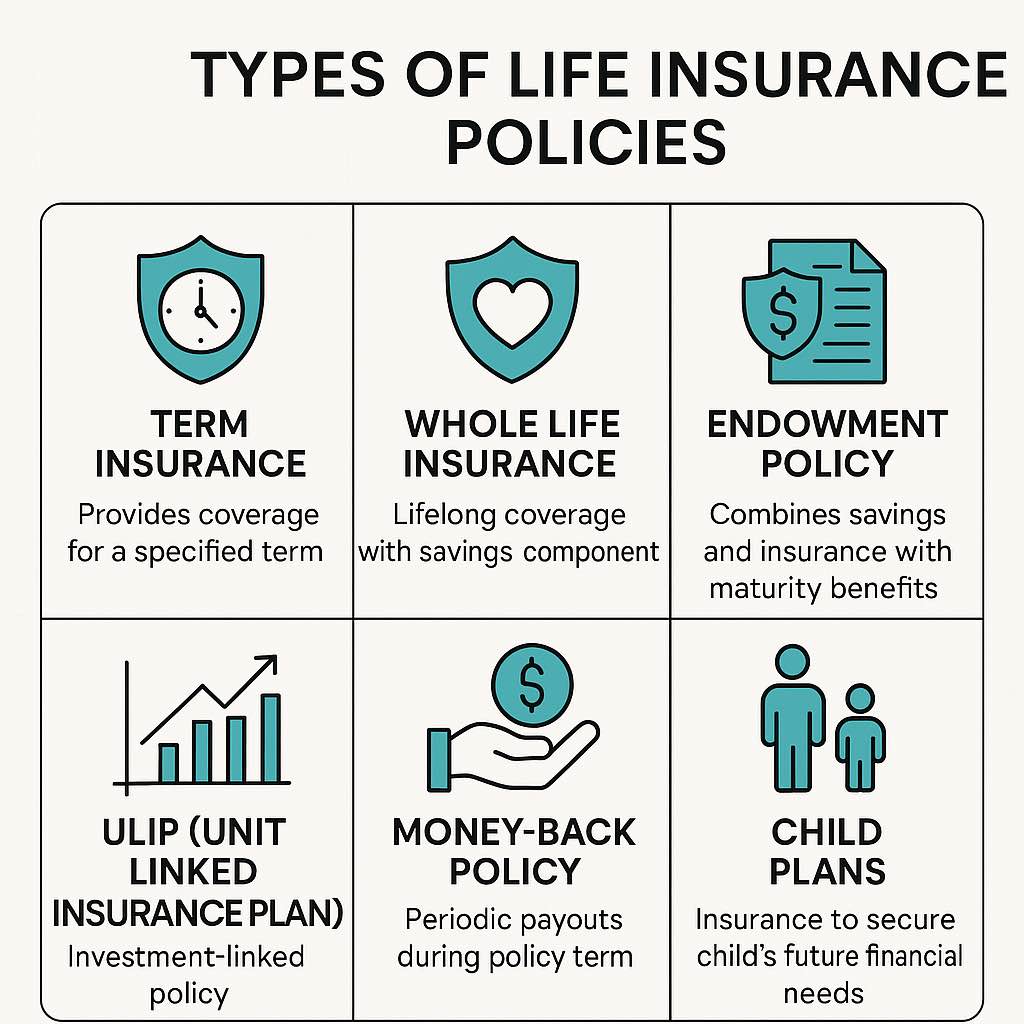
Main Types of Life Insurance Policies
- Term Life Insurance
- Pure protection cover for a specified term (e.g., 20, 30 years)
- Low premiums since there’s no savings component
- Ideal for young earners seeking maximum cover at minimal cost
- No maturity benefit, if you outlive the term, then you receive nothing
- Whole Life Insurance
- Lifetime cover with premiums payable up to a certain age (e.g., 75 or 100)
- Builds cash value over time that you can borrow against
- Premiums higher than term policies but guaranteed payout upon death
- Endowment Plans
- Combine insurance with savings—pay maturity benefit if you survive the term
- Lower death cover relative to premium
- Bonuses declared by insurer enhance returns but are not guaranteed
- Unit Linked Insurance Plans (ULIPs)
- Dual benefit of market-linked investment and life cover
- Part of your premium is invested in equity/debt funds; NAV fluctuations affect returns
- Higher charges (premium allocation, fund management, mortality)
- Lock-in period of 5 years—best for investors with medium-term horizons
- Money-Back Plans
- Periodic survival benefits during the policy term (e.g., payouts every 5 years)
- Reduces liquidity stress in mid-term but lowers death cover
- Suitable for individuals who want regular payouts
- Child Plans
- Designed to fund children’s future needs—education, marriage
- Survival benefits at key milestones
- Can combine with term cover to ensure children are protected if the parent dies
Choosing the Right Policy: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Assess Your Cover Requirement
- Calculate your family’s annual expenses and multiply by the number of years you want coverage (e.g., 20× current expenses)
- Add outstanding liabilities (home loan, personal loans, credit card debt)
- Subtract your liquid assets and existing life cover
- The result is your ideal sum assured
- Determine Your Budget
- As a rule of thumb, allocate no more than 10%–15% of your monthly income toward life insurance premiums
- Compare premium quotes for similar sum assured across insurers using aggregator platforms
- Select Policy Term
- Opt for a term that covers you until your major financial obligations are met—typically until children graduate or home loan is paid off
- Consider extending slightly beyond your planned retirement age for added protection
- Choose Policy Type Based on Goals
- Pure protection (Term) if your primary goal is maximum cover for dependents at minimal cost
- ULIP or endowment if you seek a combination of savings/investment with insurance, but be mindful of charges
- Whole life if you want lifetime cover and cash value accumulation
- Add Riders Wisely
- Critical Illness Rider: Lump-sum payout on diagnosis of specified illnesses (cancer, heart attack)
- Accidental Death Benefit: Additional sum assured if death occurs due to an accident
- Waiver of Premium: Waives future premiums if you become disabled
- Evaluate rider costs and remove unnecessary riders to avoid premium inflation
- Compare Insurer Reputation and Claims Settlement Ratio
- Aim for insurers with a claims settlement ratio (CSR) above 95% for reassurance that valid claims are honored promptly
- Review customer service ratings, premium payment options, and digital service capabilities
- Understand Tax Benefits
- Premiums up to ₹1.5 lakh per annum qualify for deduction under Section 80C
- Death benefit is tax-free under Section 10(10D)
- Review Policy Documents Thoroughly
- Read policy terms, exclusions, free look period conditions and revival rules
- Confirm waiting periods for critical illness benefits and any sub-limits
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Under-insuring: Opting for low sum assured to save on premiums leaves dependents underprotected
- Overloading on Riders: Adding multiple riders can push premiums beyond affordability, which may leads to policy lapse
- Choosing ULIPs for Short-Term Goals: ULIPs have lock-in and higher charges; not suitable for horizons under 10 years
- Ignoring Inflation: Ensure sum assured grows periodically or choose increasing cover options to combat inflation
- Not Reviewing Periodically: Life events like marriage, birth of child, change in income—warrant policy reviews and top-ups
Illustrative Example
Rahul, 29, newly married with a 10-year home loan of ₹40 lakh and monthly expenses of ₹60,000:
- Cover for 20 years of expenses: 20 × ₹7.2 lakh = ₹1.44 crore
- Home loan liability: ₹40 lakh
- Total cover required: ₹1.84 crore
- Rahul’s budget allows for a ₹1.5 crore term policy at ₹1,800/month; he supplements with a ₹34 lakh term rider for accidental death at ₹200/month
- He also adds a critical illness rider for ₹10 lakh benefit at ₹500/month
- Total monthly premium: ₹2,500
- Rahul locks in his free look review and confirms CSR of 97% with the chosen insurer
Final Checklist Before You Buy
- Calculate realistic cover need factoring in inflation
- Compare quotes across at least five insurers
- Choose pure term for protection; consider ULIP/endowment only for long-term savings goals
- Limit riders to essential ones (critical illness, accidental death)
- Verify CSR, customer reviews, digital interface and claim process
- Use free look period to reassess your decision
By following this structured approach you can confidently navigate the complex life insurance landscape and select a policy that provides both financial security for your loved ones and aligns with your long-term financial goals.
- Sunita Williams’ Secret: Astronaut Mindset That Builds Crores via SIP Investing
 Discover Sunita Williams’ astronaut mindset for wealth building: Solve crises “one bite at a time” like mutual fund SIP investing. Learn disciplined saving, risk pivots, and best mutual funds India strategies from her 27-year NASA career.
Discover Sunita Williams’ astronaut mindset for wealth building: Solve crises “one bite at a time” like mutual fund SIP investing. Learn disciplined saving, risk pivots, and best mutual funds India strategies from her 27-year NASA career. - The ₹1 Magic: Transform Pocket Change Into ₹1,378 With This Simple 52-Week Plan
 Transform your finances with India’s most popular 52-week money challenge. Save just ₹1 in week one, building to ₹52 by year-end for a total of ₹1,378. Discover the reverse challenge, practical tips, and how consistent saving habits create lasting financial freedom.
Transform your finances with India’s most popular 52-week money challenge. Save just ₹1 in week one, building to ₹52 by year-end for a total of ₹1,378. Discover the reverse challenge, practical tips, and how consistent saving habits create lasting financial freedom. - Forget 10% Salaries: Why 48% of India’s Gen Z are Starting SIPs with Just ₹500
 Discover how India’s Gen Z is building wealth with just ₹500 monthly SIPs. From ₹3 trillion in SIP inflows to 100 million active accounts, young investors are leveraging compound interest and disciplined investing to achieve financial independence without hefty salaries or trust funds.
Discover how India’s Gen Z is building wealth with just ₹500 monthly SIPs. From ₹3 trillion in SIP inflows to 100 million active accounts, young investors are leveraging compound interest and disciplined investing to achieve financial independence without hefty salaries or trust funds. - Is Your Credit Card Quietly Killing Your Score? The 30% Factor Lenders Watch Closely
 Credit utilization ratio can quietly make or break your CIBIL score. Keeping card usage below 30% signals control, not desperation. With simple moves—mid‑cycle payments, spreading spends, and requesting higher limits—you can boost approval odds and pay less interest overall today.
Credit utilization ratio can quietly make or break your CIBIL score. Keeping card usage below 30% signals control, not desperation. With simple moves—mid‑cycle payments, spreading spends, and requesting higher limits—you can boost approval odds and pay less interest overall today. - Need a Loan? Use These 7 No-Gimmick Tactics to Fix Your CIBIL Score in Just 30 Days
 Boost your CIBIL score by 50+ points in just 30 days with proven tactics. Master payment history, reduce credit utilization, and dispute errors to unlock better loan approvals and lower interest rates. No gimmicks—just real strategies that work.
Boost your CIBIL score by 50+ points in just 30 days with proven tactics. Master payment history, reduce credit utilization, and dispute errors to unlock better loan approvals and lower interest rates. No gimmicks—just real strategies that work.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.