Health insurance for families feels confusing because it mixes emotions, fine print and big money decisions; this guide makes it simple, practical and tailored to Indian households aged 25–45.
Why family cover matters
- Medical inflation in India rises much faster than salaries, so one major hospitalization can wipe years of savings; insurance transfers that risk to an insurer.
- A single family floater is easier to manage than multiple policies and premiums are eligible for tax deductions under Section 80D.
- For larger families, combining a base policy with a super top-up gives high coverage at a lower premium than buying only a high base sum insured.
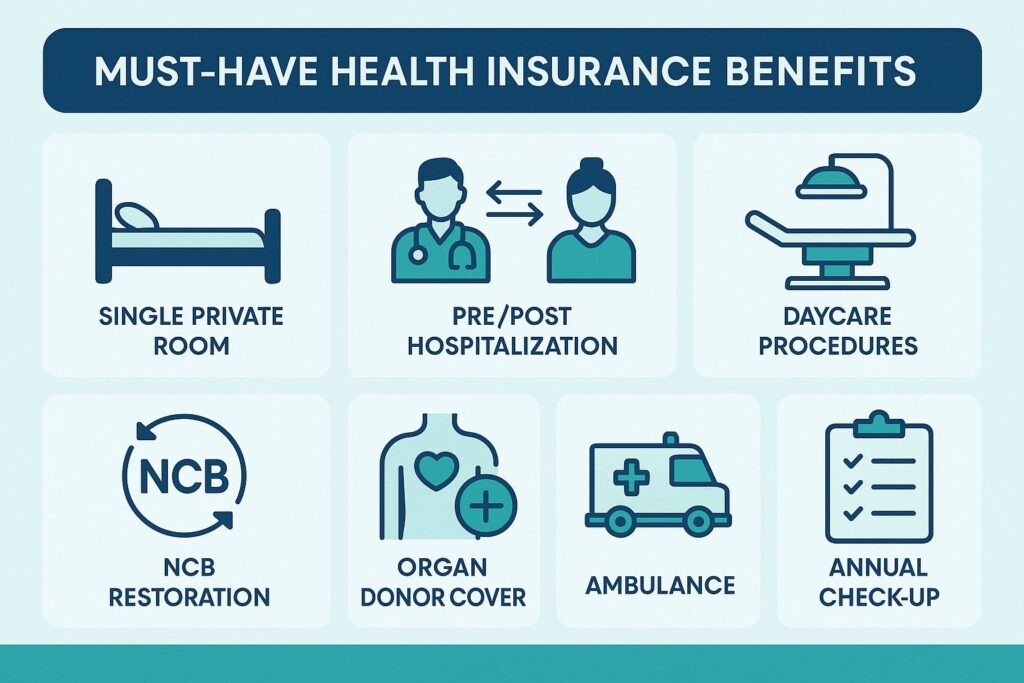
Must‑have benefits
- Room eligibility: single private room (no restrictive “1% of sum insured” caps).
- Pre/post-hospitalization: at least 60/180 days; 90/180 is better.
- Day-care/modern treatments: robotic surgery, oral chemo, angioplasty stents etc.
- No‑claim bonus (NCB): cumulative bonus that increases sum insured, not a discount-only plan.
- Restoration: automatic per insured unlimited times in a year (not just once).
- Organ donor & domiciliary cover: fees for donor surgery and at-home treatment if beds unavailable.
- Emergency ambulance and air ambulance (if budget allows).
- Mental health, AYUSH coverage and annual health check-up.
- Cashless network: large, nearby and reputable hospitals where the family lives and travels.
- PED terms: short waiting period (2–3 years), transparent underwriting for existing conditions.
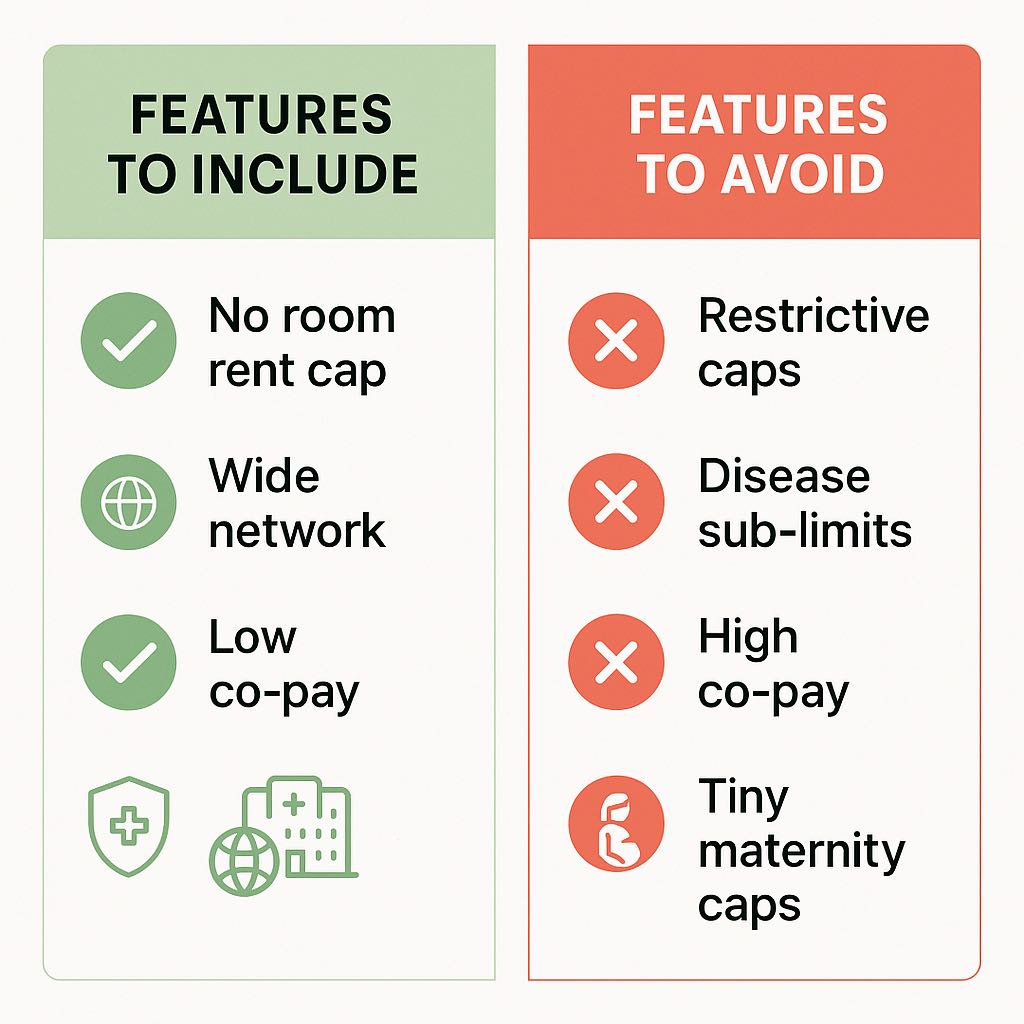
Benefits to avoid or treat with caution
- Room-rent caps and proportionate deductions.
- Disease‑wise sub‑limits (e.g. hernia not exceeding ₹50,000) unless budget forces it.
- Co‑pay above 10% for non-senior adults; it reduces claims payout.
- “Low premium, many exclusions” plans: check wordings for modern treatment limits.
- Maternity with tiny caps and long waits; buy only if planning a child and the cap fits city costs.
- Steep deductibles hidden in fine print; use them only in super top‑ups by choice.
- Very small networks or third‑party administrators (TPA) with poor service ratings.
Smart structure for a 6‑member family
Assumption used: Family of six = one couple (36 & 34), two kids (8 & 4), and two elders (63 & 60). Seniors are best insured separately to keep premiums reasonable for the younger four.
How much cover?
- Metro/Tier‑1: Adults+kids 25–50L base (or 10–15L base + 25–50L super top‑up with ₹5L deductible). Seniors: 10–20L base + 20–50L super top‑up.
- Tier‑2/3: Adults+kids 15–25L total; Seniors 10–15L + super top‑up.
Case study: plan designs by income band
The figures below are indicative bands to guide structure and features. Actual quotes vary by insurer, city, age, and medical history.
| Item | High income (metro) | Middle income (tier‑1/2) | Low income (tier‑2/3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family split | Couple+2 kids on family floater; elders on separate senior plan | Same split | Same split |
| Adults+kids cover | 15L base + 35L super top‑up (₹5L deductible) | 10L base + 25L super top‑up (₹5L deductible) | 5L base + 15L super top‑up (₹5L deductible) |
| Elders cover | 10L senior plan + 25L super top‑up (₹5L deductible) | 7.5–10L senior plan + 15–20L super top‑up | 5L senior plan + 10–15L super top‑up |
| Room entitlement | Single private room; air ambulance optional | Single private room; no air ambulance | Single room where affordable; else cap clearly understood |
| Must‑have add‑ons | NCB that increases sum insured; unlimited restoration; modern treatment cover; global emergency (optional) | NCB (sum insured growth); restoration; AYUSH; organ donor; check-up | Restoration; wider network; donor cover; check-up |
| Co‑pay | 0% adults/kids; ≤10% for seniors | 0% adults/kids; 10–20% seniors (only if premiums stretch) | 0% adults/kids; 20% seniors if needed to reduce premium |
| Maternity | Include only if planning in 2–3 yrs; cap ≥ ₹1.5–2L; 2–3 yr wait | Include only if cap ≥ ₹75k–₹1.5L and wait acceptable | Usually skip; focus on core hospitalization |
| OPD/dental | Optional rider if employer policy weak | Optional | Skip to save premium |
| Annual premium (indicative band) | Adults+kids: ₹35k–₹60k; Elders: ₹55k–₹1.2L | Adults+kids: ₹22k–₹40k; Elders: ₹40k–₹80k | Adults+kids: ₹15k–₹28k; Elders: ₹30k–₹60k |
| Why it fits | High protection for metro costs; preserves savings | Strong core cover with value riders | Essential protection within tight budget |
Note: If a senior has significant pre‑existing illnesses, consider a disease‑management plan or higher deductible super top‑up to keep premiums manageable.
Quick decision tree
- Employer cover ≥10L and includes parents? Buy a super top‑up (₹5L or ₹10L deductible) for family and a separate senior plan if parents aren’t covered.
- No employer cover? Buy a base floater first (at least 10–15L in metros) and add a super top‑up the same day.
- Expecting a child in 2–3 years? Choose maternity rider now; most plans impose a waiting period.
- Frequent private hospitals? Prioritize single-room eligibility and big cashless networks.
Step‑by‑step buying checklist
- List ages, illnesses, surgeries, regular meds of each member; disclose truthfully.
- Shortlist 3–4 insurers with strong cashless networks near home/work and cities parents reside in.
- Prefer plans with single private room entitlement, 60/180 or 90/180 pre/post cover and modern treatment inclusion.
- Compare restoration (per insured, multiple times), NCB (sum boosted, not premium discount only) and PED waiting (2–3 years).
- Price out a base + super top‑up vs a high base—choose the cheaper combo with same overall cover.
- For seniors, compare co‑pay and disease sub‑limits; pay a bit more to reduce co‑pay if feasible.
- Do a pre‑policy medical if asked; it prevents disputes later.
- Read exclusions (obesity, IVF, experimental treatments, hazardous sports); ensure they match your lifestyle.
- Save soft copies of policy, e‑cashless card and insurer’s claim helpline; set calendar reminders for renewal and health check-ups.
- After purchase, complete e‑card registration with the hospital desk you prefer; test the cashless desk process with a non-emergency visit if possible.

Do’s and don’ts
- Do buy early (before 35) to lock better premiums and shorter waits.
- Do keep adults+kids and seniors on separate policies to avoid premium spikes.
- Do use super top‑ups to lift cover affordably.
- Don’t chase the lowest premium if it adds room caps, sub‑limits or high co‑pay.
- Don’t hide medical history; it risks claim rejection.
- Don’t forget portability—after 3+ years of continuous cover, you can shift to a better plan retaining credits.
Example claims math (how it plays out)
- Hospital bill: ₹7.5L (single private room).
- Base policy: ₹10L floater with 90/180 pre/post; no room cap.
- Payout: Room + procedures eligible fully; pre (₹30k) and post (₹70k within 180 days) covered; OOP limited to non‑medical consumables unless add‑on chosen.
- With room‑rent cap policy (e.g., 1% of SI = ₹10k/day): proportionate deduction could cut payout by 20–40%—this is why single-room eligibility matters.
Common rider picks (worth the money)
- NCB that increases sum insured (up to 100–200%).
- OPD & consumables (if you prefer minimal OOP).
- Air ambulance (for frequent inter‑city travel).
- Critical illness rider (lump sum) for income protection—not a substitute for base mediclaim.
Renewal tips
- Track claims experience; if you faced sub‑limits, port to a plan without them at renewal.
- Increase sum insured or add super top‑up when family milestones change (new baby, parents moving in).
- Use the cashless network whenever possible; reimbursements take longer and need more paperwork.
Friendly FAQs
- Is a ₹5L cover enough? Only in small towns and only with a super top‑up on top; metro families should target 25L+ combined.
- Employer cover is 5L—buy more? Yes; employer covers change and end with the job.
- Can I add newborns mid‑term? Most plans allow it from day 1–90 (check wording); notify the insurer and pay prorated premium.
- Sunita Williams’ Secret: Astronaut Mindset That Builds Crores via SIP InvestingDiscover Sunita Williams’ astronaut mindset for wealth building: Solve crises “one bite at a time” like mutual fund SIP investing. Learn disciplined saving, risk pivots, and best mutual funds India strategies from her 27-year NASA career.
- The ₹1 Magic: Transform Pocket Change Into ₹1,378 With This Simple 52-Week PlanTransform your finances with India’s most popular 52-week money challenge. Save just ₹1 in week one, building to ₹52 by year-end for a total of ₹1,378. Discover the reverse challenge, practical tips, and how consistent saving habits create lasting financial freedom.
- Forget 10% Salaries: Why 48% of India’s Gen Z are Starting SIPs with Just ₹500Discover how India’s Gen Z is building wealth with just ₹500 monthly SIPs. From ₹3 trillion in SIP inflows to 100 million active accounts, young investors are leveraging compound interest and disciplined investing to achieve financial independence without hefty salaries or trust funds.
- Is Your Credit Card Quietly Killing Your Score? The 30% Factor Lenders Watch CloselyCredit utilization ratio can quietly make or break your CIBIL score. Keeping card usage below 30% signals control, not desperation. With simple moves—mid‑cycle payments, spreading spends, and requesting higher limits—you can boost approval odds and pay less interest overall today.
- Need a Loan? Use These 7 No-Gimmick Tactics to Fix Your CIBIL Score in Just 30 DaysBoost your CIBIL score by 50+ points in just 30 days with proven tactics. Master payment history, reduce credit utilization, and dispute errors to unlock better loan approvals and lower interest rates. No gimmicks—just real strategies that work.




